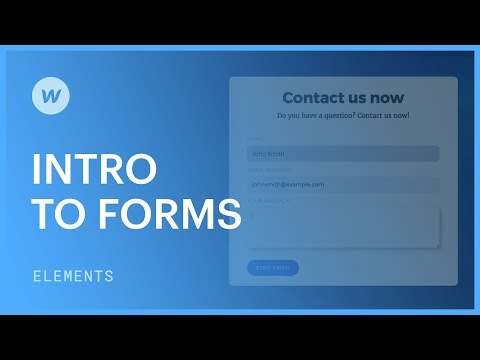
Forms of course can capture valuable information. Their design and functionality can easily make or break the user experience. In this article, we will be covering five things related to forms: adding a form, anatomy of a form, configuring form elements, success and error messages, and form submissions. To start, we will add a form block to our project. We can do this by going to the elements panel and dragging the form block onto the canvas. The form block comes with some essentials that serve as a good starting point. It is important to start with the form block rather than individual form elements because the form block itself is required to capture the data collected when the form is filled out. Although you can delete elements inside the form block and start from scratch, the form block is our starting point. Let's take a closer look at the anatomy of the form block. To do this, make sure the navigator is visible. The form wrapper is the top-level element that takes up the full width of its parent element, in this case, the container. Inside the form wrapper, we can see three elements: the form, success message (displayed when the form is successfully submitted), and error message (displayed if there is a problem submitting the form). On the canvas, under the form element, we can see field labels and text fields for name and email. There is also a submit button. These elements are included by default in a form block. Now, let's talk about configuring specific elements. For example, if we double click on the name field, we can access input settings. These settings include the name field (used internally for identification in form submissions), placeholder text (text displayed before someone types something in the field), type of text (such as...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing When Form 8655 Website